Deep Understanding of Ethereum
深入理解以太坊
专有名词
EOA, Contract Accounts, Account state, Account nonce, World state, Transaction, Receipt, Block, Uncle block, Nonce, Gas, Gas price, Gas Price Oracle
Zero Knowledge Proof, EVM, Message, RLP, MPT (Merkle Patricia Tree), Patricia Trie, Merkle Tree, Whisper, Light Ethereum Subprotocol, Swarm, LLL, Sperpent, Mutan, Solidity, EIPs(ERC20, ERC721)
Uncle block
Uncle blocks (or Ommer) are created when two or more miners create blocks at nearly the same time. Only one block can be mined and accepted as canonical on the blockchain. The others are uncle blocks, which are not included but still provide a reward to their miners for the work done.
在比特币网络中,uncle block 是没有奖励的;但在以太坊网络中,uncle block 有奖励,并且一个区块最多能引用 2 个 uncle block;
- uncle block reward 是奖励给 uncle block 的矿工的,前提是被确认的区块引用了这个 uncle block
- 包含了 uncle block 的区块,会获得一个额外的奖励,这个奖励是 uncle block reward 的 1/32
主要作用是:提高网络安全性,提高矿工的积极性
- 以太坊为什么要设置区块的叔块奖励?
- There are two uncle rewards
在以太坊升级 PoS 后,uncle block 还有吗?
- Block header structure change under the Merge to Proof of Stake?
- How The Merge Impacts Ethereum’s Application Layer
总结下来,以太坊从 PoW 升级到 PoS 后,部分和 PoW 共识相关的字段就无用了,但是出于兼容和一致性的考虑,这些字段会被设置默认值,其中 uncle (Ommer) 是其中一项。
In order to minimize disruption to tooling and infrastructure, these fields are set to 0, or their data structure’s equivalent, rather than being entirely removed from the data structure. The full changes to block fields can be found in EIP-3675.
账户模型
以太坊中,账户分为:外部账户(EOAs)和合约账户(contract account)
参考
- 账户
EOAs
EOAs-外部账户(external owned accouts)是由人们通过私钥创建的账户。 是真实世界的金融账户的映射,拥有该账户私钥的任何人都可以控制该账户。 如同银行卡,到ATM机取款时只需要密码输入正确即可交易。 这也是人类与以太坊账本沟通的唯一媒介,因为以太坊中的交易需要签名, 而只能使用拥有私有外部账户签名。
外部账户特点总结:
- 拥有以太余额。
- 能发送交易,包括转账和执行合约代码。
- 被私钥控制。
- 没有相关的可执行代码。
合约账户
含有合约代码的账户。 被外部账户或者合约创建,合约在创建时被自动分配到一个账户地址, 用于存储合约代码以及合约部署或执行过程中产生的存储数据。 合约账户地址是通过SHA3哈希算法产生,而非私钥。 因无私钥,因此无人可以拿合约账户当做外部账户使用。 只能通过外部账户来驱动合约执行合约代码。
// 合约地址生成算法
// sender: 指交易的发起者的地址
// nonce: 指该交易的随机数
Keccak256(rlp([sender,nonce])[12:])
合约账户特点总结:
- 拥有以太余额。
- 有相关的可执行代码(合约代码)。
- 合约代码能够被交易或者其他合约消息调用。
- 合约代码被执行时可再调用其他合约代码。
- 合约代码被执行时可执行复杂运算,可永久地改变合约内部的数据存储。
账户抽象
在最近的 EIP 中提出了账户抽象的概念(关于账户抽象看 Account abstraction)
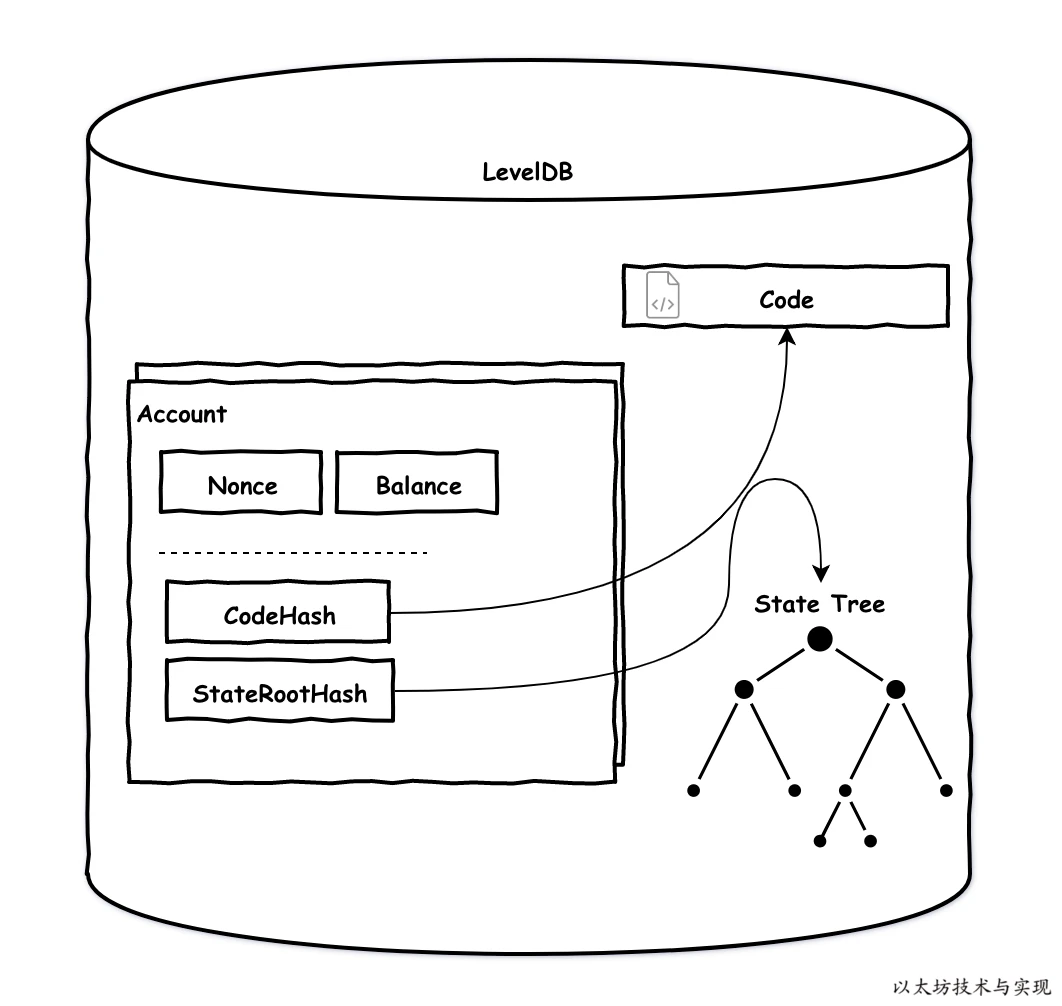
账户数据结构
type Account struct {
Nonce uint64
Balance *big.Int
Root common.Hash
CodeHash []byte
}

以太坊中的交易
指由一个外部账户转移一定资产给某个账户, 或者发出一个消息指令到某个智能合约
参考资料
- 以太坊技术与实现 - 交易
- 区块链架构之美 - EVM / Transaction
- 深入理解以太坊
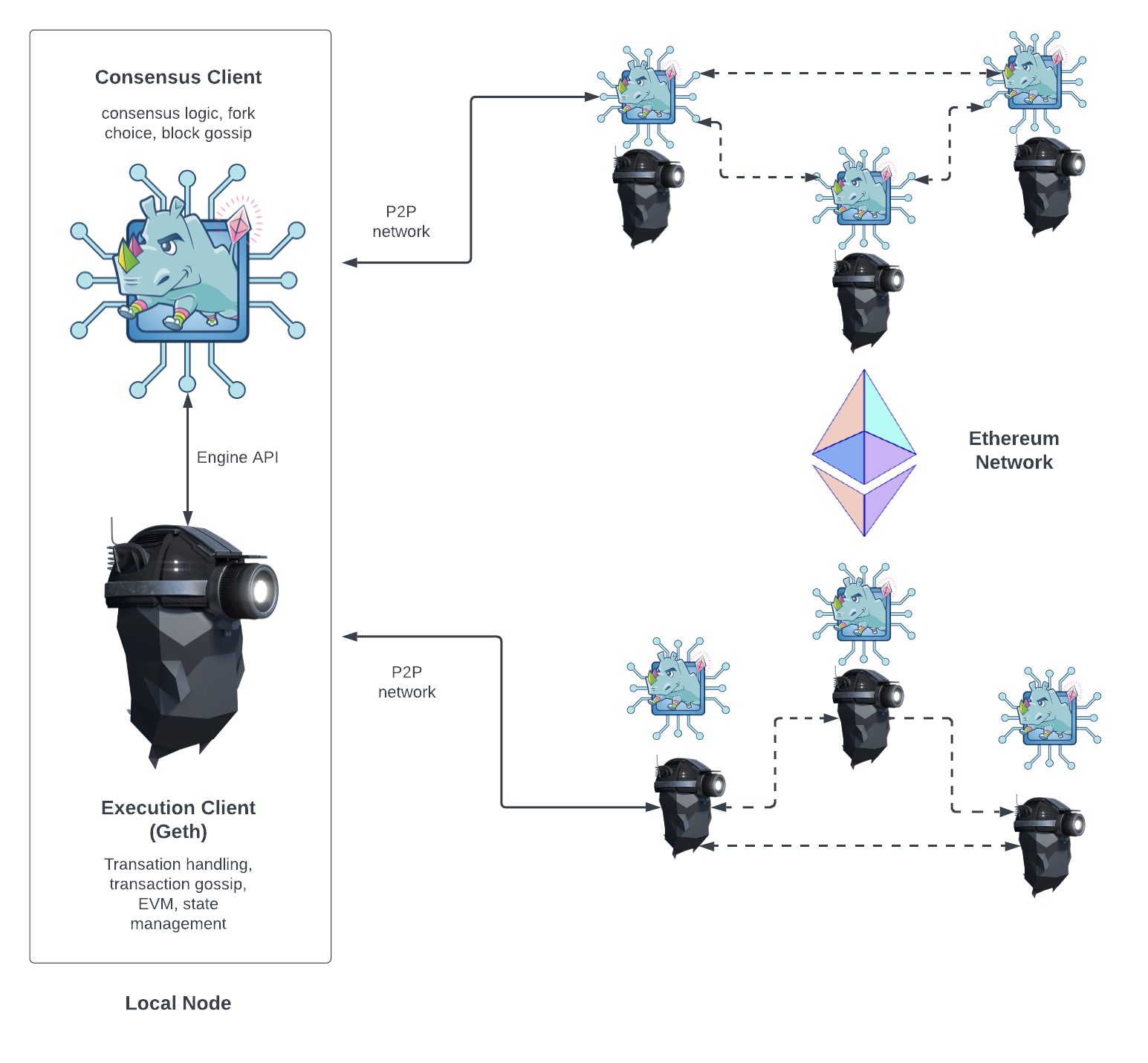
Ethereum Node Architecture
在 The Merge 之后,以太坊节点有两部分组成:执行客户端 (EL, Execution Client) 和共识客户端 (CL, Consensus Client):
- EL 负责交易处理,交易广播,状态管理以及对 EVM 的支持
- Geth 是一种 EL 的实现,还有其他的实现,比如 Parity
- CL 负责区块创建,区块广播和共识逻辑
- EL 和 CL 之间的通信使用的是 Engine API, 基于本地的 JSON-RPC
- CL 是在
The Merge 之后开始生效的,正式从 PoW 切换到 PoS
他们之间的关系如下图

几个规范需要关注
- Execution API
- Execution Specs
- Engine API
- Consensus Specs
EVM
Event logs
TODO
- https://ethereum.org/en/developers/docs/evm/
Storage Layouts in EVM
深入理解 EVM 的存储布局非常重要,因为它直接影响到合约的 gas 消耗,以及合约的安全性。
Solidity 中有三种内存类型:storage, memory, calldata
- memory 类型的变量和参数,用在函数的内部,只在函数执行期间存在,函数执行完毕后,内存被清空
- calldata 类型是在外部调用函数时,传递的参数,只读,不能修改
- storage 类型的变量,用来存储合约的状态,永久存在,直到合约被销毁
storage memory layout
每个合约都有自己的存储区域,它是一个可以持久化、读写的内存区域,合约只能访问自己的内存空间,不能访问其他合约的;合约的存储空间被划分为一个个的存储槽,每个槽的大小为 256 位,每个槽都有一个唯一的索引,从 0 开始,每个槽都可以存储一个 256 位的值,也就是说,每个槽都可以存储一个 uint256 类型的值,或者 32 个字节的值;并且 EVM 一次需要直接访问 32 字节的数据,槽的总数是 2^256 大小。
这个抽象非常类似虚拟内存,EVM 会记录每个合约中槽的使用情况,最开始槽是没有初始化的
字节序:大端和小端;在 EVM 中 bytes 和 string 使用的是大端;其他类型用的是小端
- 如果一个类型不足 32 bytes,会被填充到 32 bytes;但是填充会浪费内存空间,但是带来了 gas 的节约,因为读写成本更低
- 但是在某些情况下,会把紧邻的不足 32 bytes 的变量包装在一起,可以节省内存空间,但是会增加 gas 消耗,因为读写成本更高,需要做更多的位运算
References
Wallet
作为用户,Wallet 是区块链的入口;现阶段主流的 Wallet 类型有:HD Wallet,MultiSig wallet,Custodial wallet,Hardware wallet,Paper wallet,MPC Wallet 等。作为开发者,HD Wallet、MultiSig Wallet、MPC Wallet 是需要重点掌握的。
HD wallet
钱包是用来存钱的,在区块链中,我们的数字资产都会对应到一个账户地址上, 只有拥有账户的钥匙(私钥)才可以对资产进行消费(用私钥对消费交易签名)。
他们之间的关系如下:
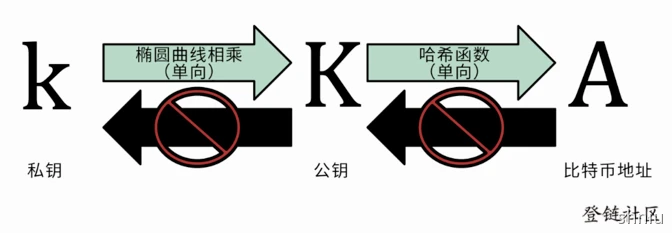

私钥通过椭圆曲线生成公钥, 公钥通过哈希函数生成地址,这两个过程都是单向的; 所以,数字钱包实际是一个管理私钥(生成、存储、签名)的工具,注意钱包并不保存资产,资产是在链上的。
生成私钥的本质是在 1 到 2^256 之间选一个数字:生成密钥的第一步也是最重要的一步,是要找到足够安全的熵源,即随机性来源,只要选取的结果是不可预测或不可重复的
HD, Hierarchical Deterministic, 叫做分层确定性钱包,是一种可以从单个种子(seed)衍生出一系列私钥的钱包结构,这些私钥都可以被根种子所控制,这样就可以用一个种子来管理多个账户。
在 Mastering Bitcoin 中,有一章是来介绍 Wallet 的,有必要看一下:Mastering Bitcoin - Wallet, 中文版看这里
HD 钱包允许我们使用一个密钥管理很多个衍生私钥,进而控制多个地址,bip32 规范中使用一种树形结构来进行管理。
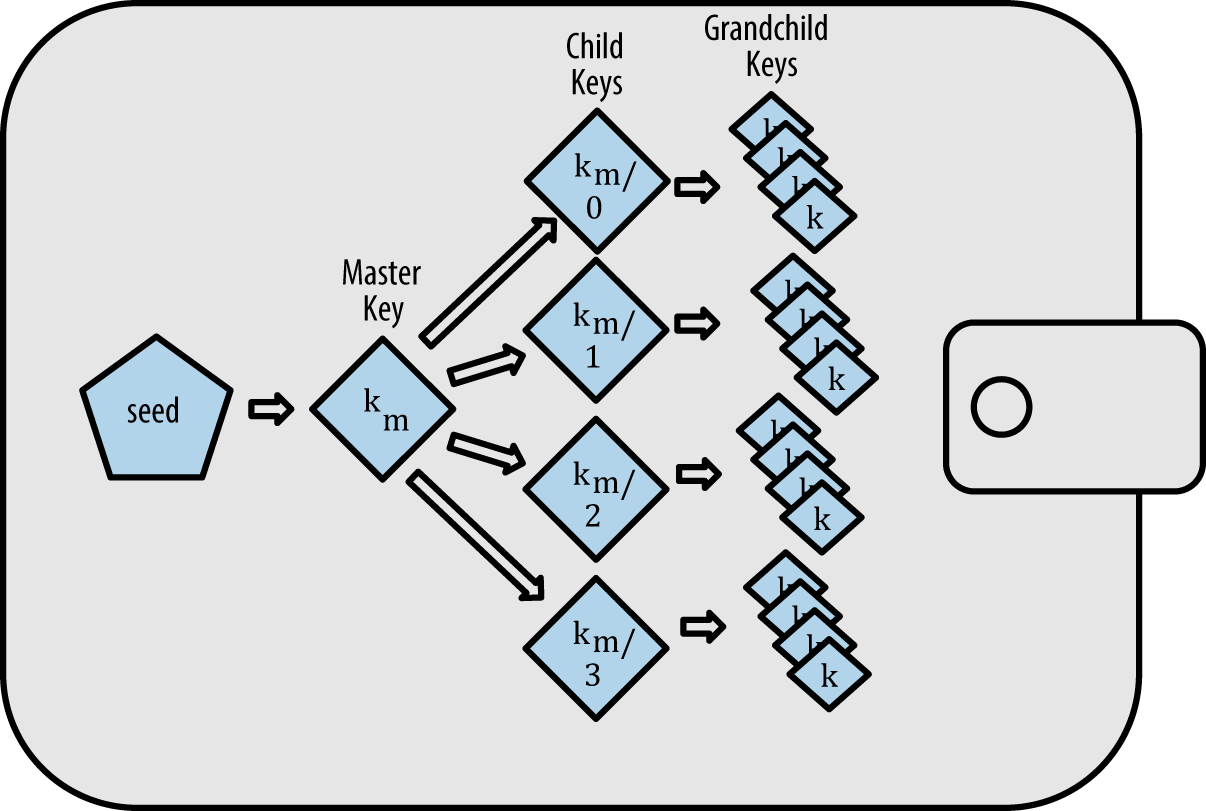

关于 HD wallet 有一系列规范:
bip39
bip39 规范主要关于生成确定性密钥的助记码,使用一组预定义的单词来表示一串随机数,这样就可以方便的记忆和传输。主要包含两部分:生成助记码和从主机码转成二进制私钥种子。
我们来看看 bip39 的技术细节
如何生成助机词
- Create a random sequence (entropy) of 128 to 256 bits.
- Create a checksum of the random sequence by taking the first (entropy-length/32) bits of its SHA256 hash.
- Add the checksum to the end of the random sequence.
- Split the result into 11-bit length segments.
- Map each 11-bit value to a word from the predefined dictionary of 2048 words.
- The mnemonic code is the sequence of words.
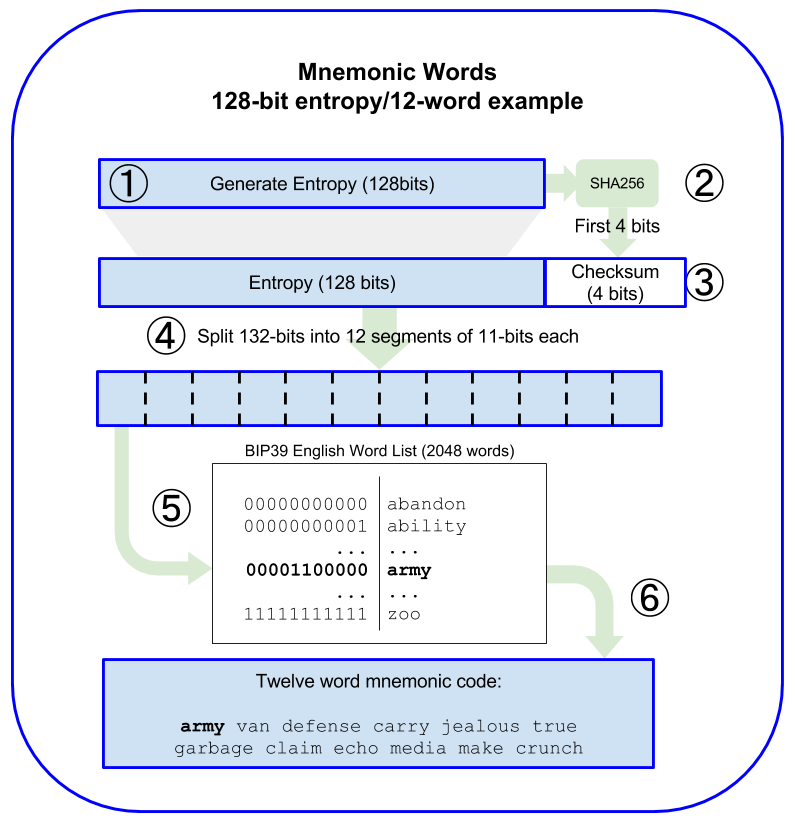

随机熵和单词长度的关系:
| Entropy (bits) | Checksum (bits) | Entropy + checksum (bits) | Mnemonic length (words) |
|---|
| 128 | 4 | 132 | 12 |
| 160 | 5 | 165 | 15 |
| 192 | 6 | 198 | 18 |
| 224 | 7 | 231 | 21 |
| 256 | 8 | 264 | 24 |
用助记词生成种子
- The first parameter to the PBKDF2 key-stretching function is the mnemonic produced from step 6.
- The second parameter to the PBKDF2 key-stretching function is a salt. The salt is composed of the string constant “mnemonic” concatenated with an optional user-supplied passphrase string.
- PBKDF2 stretches the mnemonic and salt parameters using 2048 rounds of hashing with the HMAC-SHA512 algorithm, producing a 512-bit value as its final output. That 512-bit value is the seed.
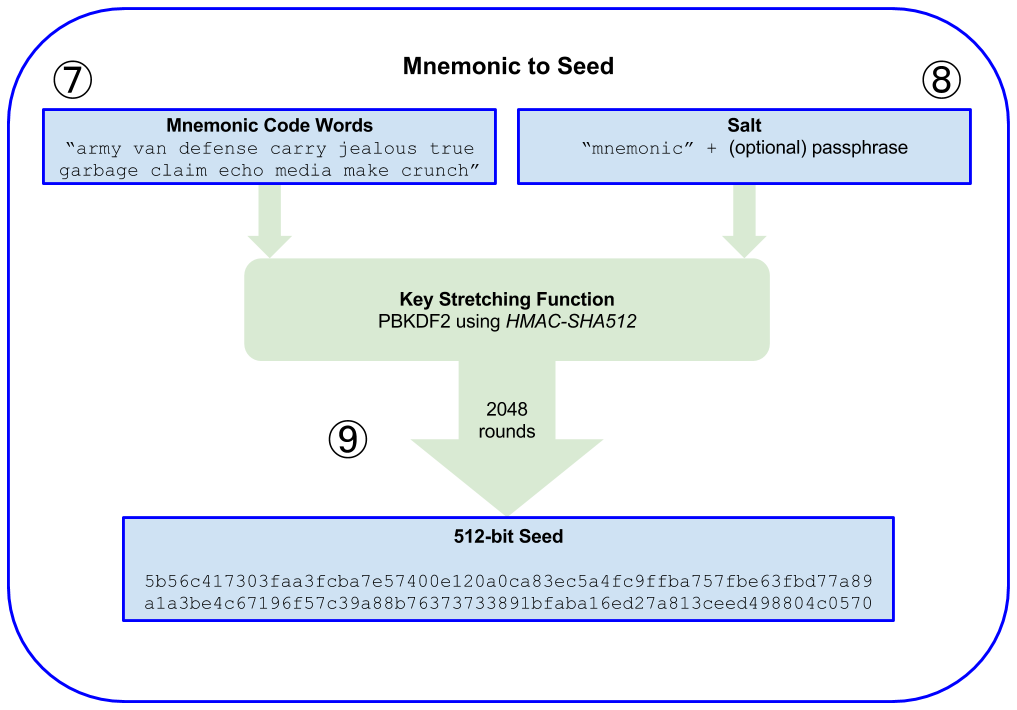

参考实现:
源码解析
func NewEntropy(bitSize int) ([]byte, error) {
// 验证位数在 128 到 256 之间,并且是 32 的倍数
if err := validateEntropyBitSize(bitSize); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
entropy := make([]byte, bitSize/8)
// 这里使用的是 crypto/rand 包,而不是 math/rand 包,因为 math/rand 包是伪随机数生成器
// 这里显然需要一个真随机数生成器
_, _ = rand.Read(entropy)
return entropy, nil
}
// 用法
entropy, _ := bip39.NewEntropy(256)
mnemonic, _ := bip39.NewMnemonic(entropy)
seed := bip39.NewSeed(mnemonic, "hello")
总结一下:bip39 的主要作用就是把随机生成的 seed 转成助记词,方便记忆、传输等,不管是导入、导出还是备份都非常方便,并且从助记词也可以还原出 seed。
bip32 & bip44
从种子生成钱包
上面了解了 bip39,通过 bip39 我们可以获取一个助记词序列,它本质上是一个随机数,这个随机数被用来当作 seed 来生成私钥。bip32 规范主要是定义了从 seed 生成私钥的过程,它定义了一种树形结构来管理私钥,这种树形结构的每个节点都有一个索引,这个索引可以用来生成子节点,这样就可以方便的管理多个私钥。
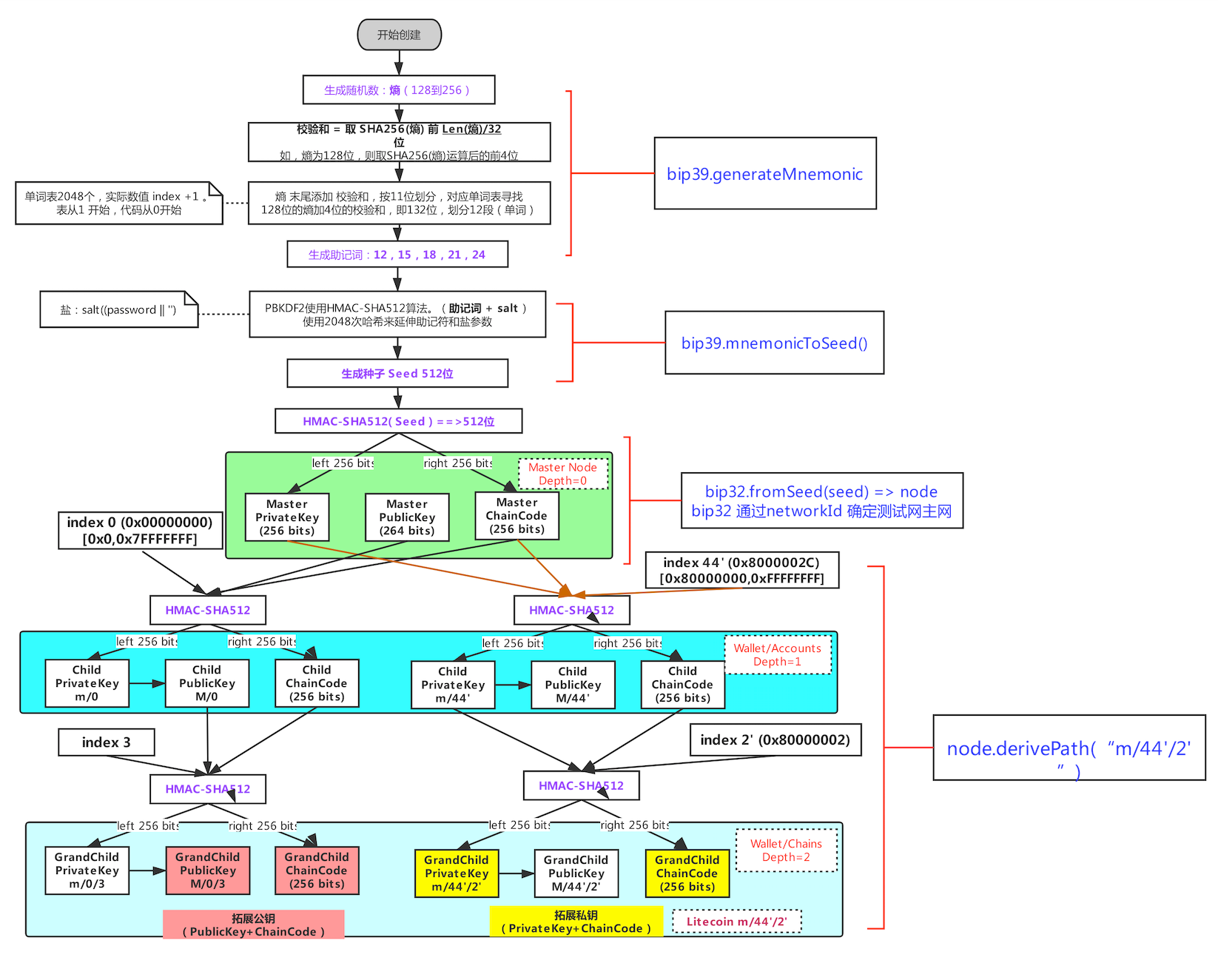

关于 extended key 也可以看这里:extended keys
参考实现
Keys 和 Addresses
在上面介绍的几个 bip 规范中,其实少了一些细节,比如私钥如何生成公钥?公钥如何生成地址?不同的链使用的算法都一样吗?…
关于这些问题可以参考这篇文章:Mastering Bitcoin - Keys and Addresses
| Chain | Private Key -> Public Key | Compressed Public Key ? | Public Key -> Address | Address Format |
|---|
| BTC | ECDSA (ecc Secp256k1) | Yes | SHA256 + RIPEMD160 | Base58 |
| ETH | ECDSA (ecc Secp256k1) | Yes | Keccak256 | Hex |
| BNB | ECDSA (ecc Secp256k1) | Yes | Keccak256 | Bech32 |
对于地址生成算法,不同的链不太一样
- Bitcoin 采用 SHA256 + RIPEMD160, 然后再进行 Base58 编码
- Ethereum 采用 Keccak256, 然后再进行 Hex 编码
- 对公钥做 Keccak-256 哈希运算,然后取最后的 40 位 16 进制字符
实现一个支持多链的 HD 本地钱包
一些想法
- 这个本地钱包,我们暂时叫他 hdkms,后面都这么叫
- hdkms 支持管理多个钱包,可以通过指定 name 来区分不同的 hd wallet
- wallet1 -> mnemonic -> seed -> master private key -> local keystore file1
- wallet2 -> mnemonic -> seed -> master private key -> local keystore file2
- hdkms 支持导入助记词、私钥
- hdkms 支持导出助记词、私钥
- hdkms 支持生成地址,并且可以指定 index
- hdkms 可以查看 address 的余额
- hdkms 支持多链
- 比如 Bitcoin, Ethereum, Binance Smart Chain etc.
- hdkms 可以离线签署交易,生成签名后的交易数据
- 支持 native token 的 transfer
- 支持 erc20
- 支持 NFT
- 支持任意类型的合约
- hdkms 可以在线广播交易
- hdkms 一些高级功能
- 支持 event 监听
- 支持动态手续费,比如 gas fee,network fee 等
- …
# 考虑怎么使用
# 1. 提供命令行工具,比如 hd-kms
# 创建钱包
hdkms wallet generate --wallet-name test1 --passphase 123456
hdkms wallet import --wallet-name test1 --mnemonic "" --passphase 123456
$ hdkms wallet export --wallet-name test1
$ {"mnemonic": "xxx", "passphase": ""}
TODOs